Finite Element Analysis (FEA)
Finite Element Analysis (FEA) is a computer-based technique that predicts how real-world objects and systems will react to forces, vibrations, heat, and other physical effects. By breaking a complex object into a mesh of smaller “finite elements,” engineers can test designs virtually, identify weaknesses, and make informed decisions before creating costly prototypes.
How FEA Works
- Discretization: Break the object into a mesh of elements (triangles, tetrahedrons, or hexahedrons).
- Mathematical Equations: Apply physical laws to each element to model behavior.
- Stiffness Matrix Formation: Combine equations into a stiffness matrix linking nodes.
- Computational Solution: Solve the matrix to predict response under applied conditions.
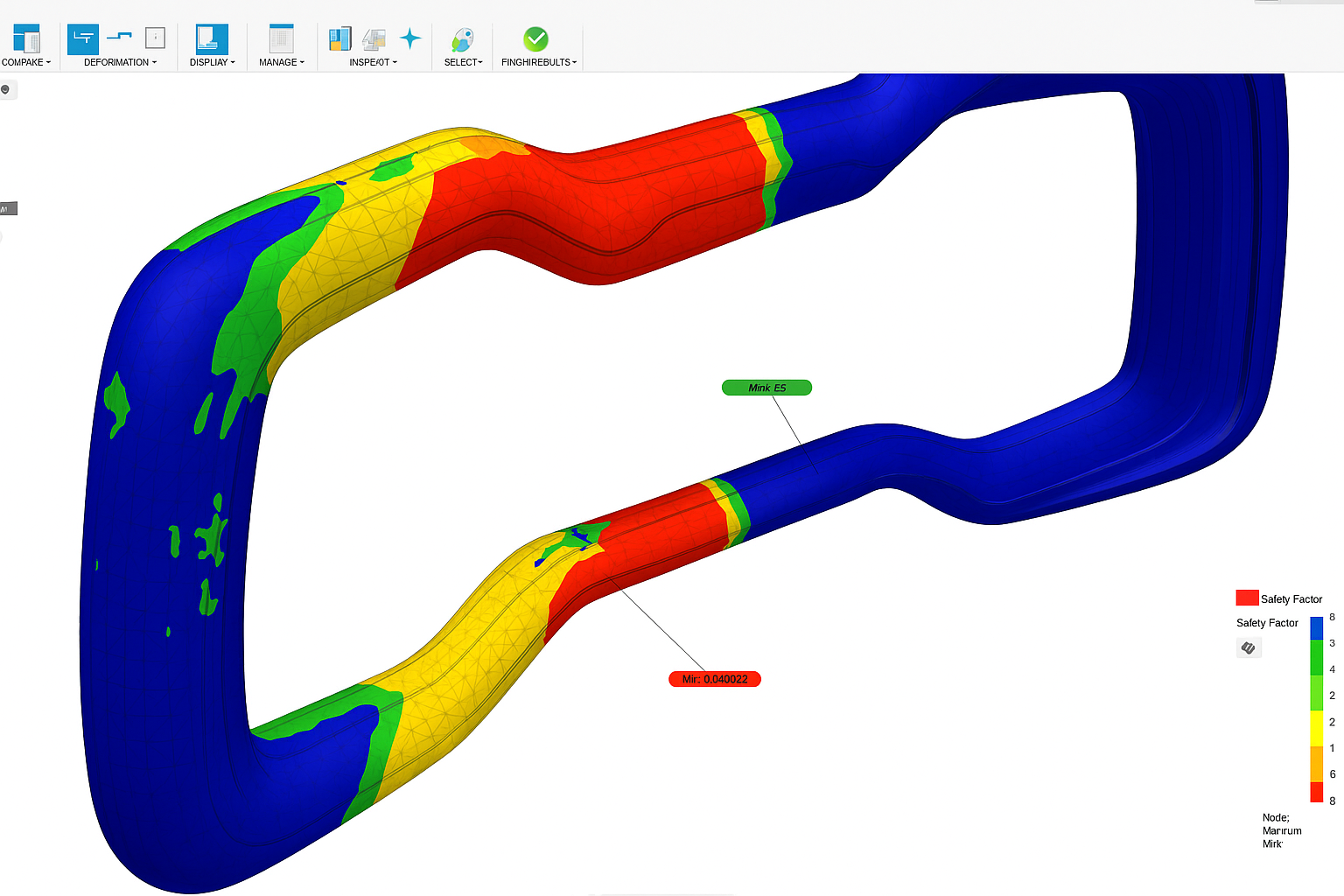
Benefits of FEA
Cost & Time Savings
Reduce physical prototypes using virtual simulation.
Informed Design
Understand complex behavior for smarter decisions.
Flaw Detection
Find stress concentrations before production.
Complex Analysis
Handle complex geometry, materials, and loads.
Applications of FEA
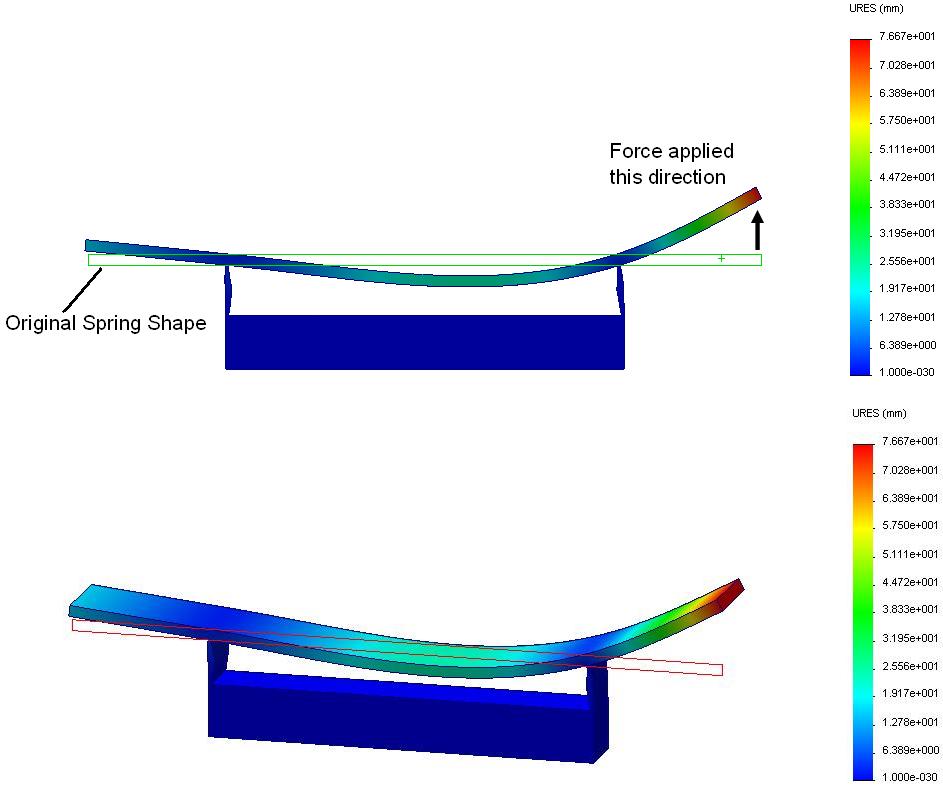
- ✔ Structural Analysis: Stress, strain, deflection, and vibration checks.
- ✔ Heat Transfer: Thermal distribution and temperature performance.
- ✔ Fluid Dynamics: Flow patterns, turbulence, and fluid-structure interaction.
- ✔ Electromagnetics: Field simulation and optimization.