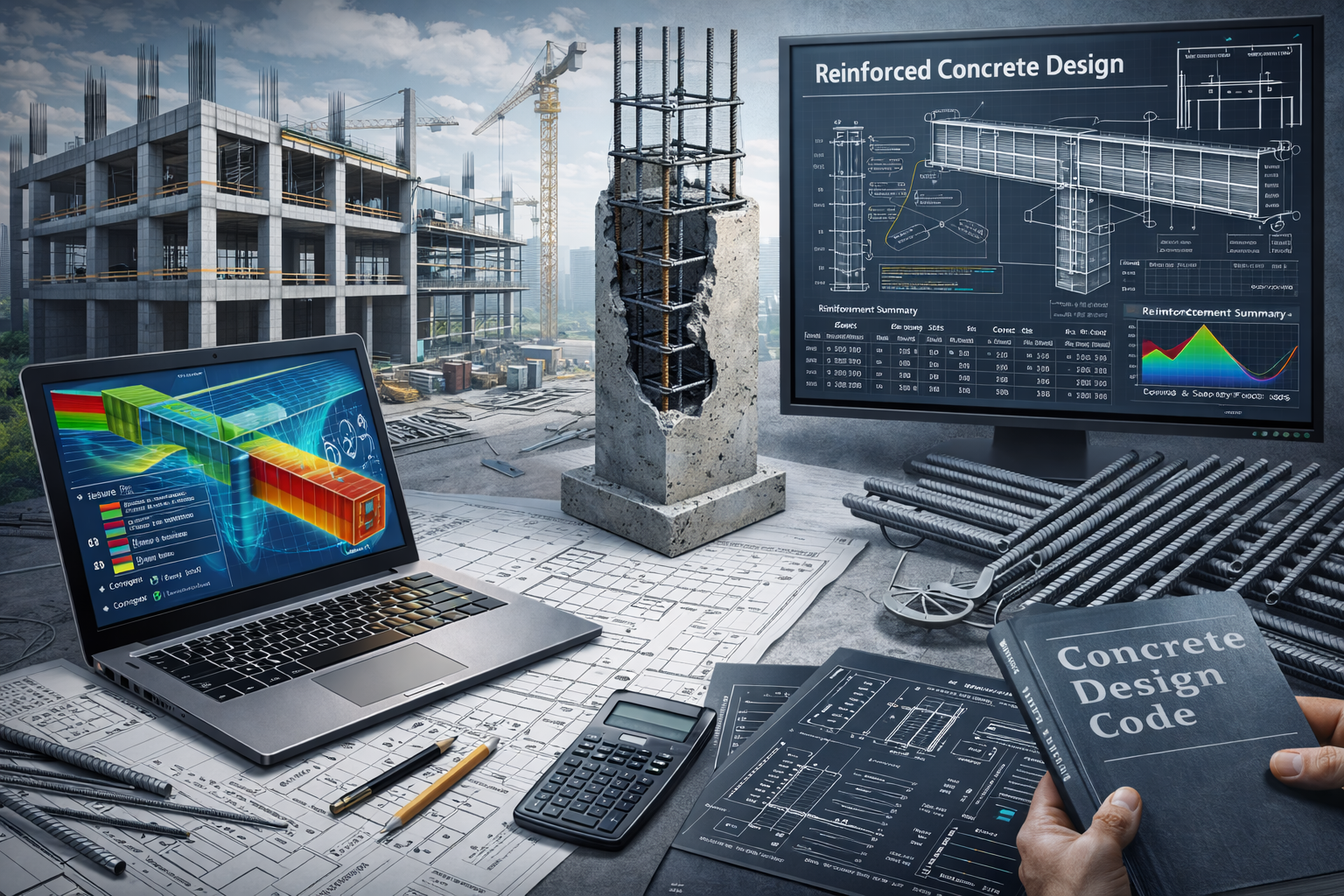
What is Reinforced Concrete?
Reinforced Concrete (RC) is concrete strengthened with steel reinforcement to improve tensile capacity. Steel reinforcement resists tension while concrete carries compression, resulting in a durable, economical, and versatile structural system.

Importance of Reinforcement
Concrete has low tensile strength and cracks under small tensile loads. Reinforcement absorbs tensile forces, ensuring safe and predictable structural behavior.
Applications of RC
RC is widely used in buildings, bridges, slabs, beams, columns, walls, and foundations. Plate-type members resist loads in multiple directions, while linear members resist axial and bending forces.
Typical Cross-Sections
Columns are typically square, rectangular, or circular. Beams are usually rectangular, while bridge girders may be T-shaped or I-shaped to optimize material efficiency.

Reinforced Concrete Design Software
Modern RC design software enables engineers to model, analyze, and design reinforced concrete members efficiently while ensuring compliance with international design codes.
These tools reduce manual errors, accelerate design cycles, and improve constructability through accurate reinforcement detailing and documentation.
Benefits of Reinforced Concrete
Reinforced concrete offers durability, fire resistance, and flexibility in architectural form. It supports long spans, heavy loads, and resilience against wind, seismic forces, and environmental exposure.